Kubernetes Informer - Reflector 篇
Mar 7, 2021 17:30 · 3436 words · 7 minute read

什么是 Informer?
Informer(也叫做 SharedInformer)是 Kubernetes 控制器(controller)中的模块,是控制器调谐循环(reconcile loop)与 Kubernetes apiserver 事件(也就是 etcd 中 Kubernetes API 数据变化)挂接的桥梁,我们通过 apiserver 增删改某个 Kubernetes API 对象,该资源对应的控制器中的 Informer 会立即感知到这个事件并作出调谐。
先大致看一眼源码 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/shared_informer.go#L168-L174:
// SharedIndexInformer provides add and get Indexers ability based on SharedInformer.
type SharedIndexInformer interface {
SharedInformer
// AddIndexers add indexers to the informer before it starts.
AddIndexers(indexers Indexers) error
GetIndexer() Indexer
}
https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/shared_informer.go#L257-L301
type sharedIndexInformer struct {
indexer Indexer
controller Controller
processor *sharedProcessor
cacheMutationDetector MutationDetector
listerWatcher ListerWatcher
// objectType is an example object of the type this informer is
// expected to handle. Only the type needs to be right, except
// that when that is `unstructured.Unstructured` the object's
// `"apiVersion"` and `"kind"` must also be right.
objectType runtime.Object
// resyncCheckPeriod is how often we want the reflector's resync timer to fire so it can call
// shouldResync to check if any of our listeners need a resync.
resyncCheckPeriod time.Duration
// defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod is the default resync period for any handlers added via
// AddEventHandler (i.e. they don't specify one and just want to use the shared informer's default
// value).
defaultEventHandlerResyncPeriod time.Duration
// clock allows for testability
clock clock.Clock
started, stopped bool
startedLock sync.Mutex
// blockDeltas gives a way to stop all event distribution so that a late event handler
// can safely join the shared informer.
blockDeltas sync.Mutex
}
嵌套的 SharedInformer 定义中注释有点多,就不贴源码了 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/shared_informer.go#L34-L166
如何使用 Informer?
只需寥寥几行代码即可在自己的项目(一般都是自定义控制器)中使用 client-go 库的 Informer 包:
import (
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
"k8s.io/client-go/informers"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"
)
kubeClient, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(cfg)
stopCh := make(chan struct{})
defer close(stopCh)
sharedInformerFactory := informers.NewSharedInformerFactory(kubeClient, time.Minute)
informer := sharedInformerFactory.Core().V1().Pods().Informer()
informer.AddEventHandler(cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func() {
// TODO
},
UpdateFunc: func() {
// TODO
},
DeleteFunc: func() {
// TODO
}
})
go sharedInformerFactory.Start(stopCh)
- 实例化一个 Kubernetes 资源 ClientSet
- 实例化一个 SharedInformer 对象
- 得到具体 Pod 资源的 Informer 对象
- 为 Informer 添加增改删事件的回调方法
- 使用一个单独的 goroutine 启动 Informer,
stopCh用于在进程退出前通知 Informer 优雅退出
深入挖掘 Informer
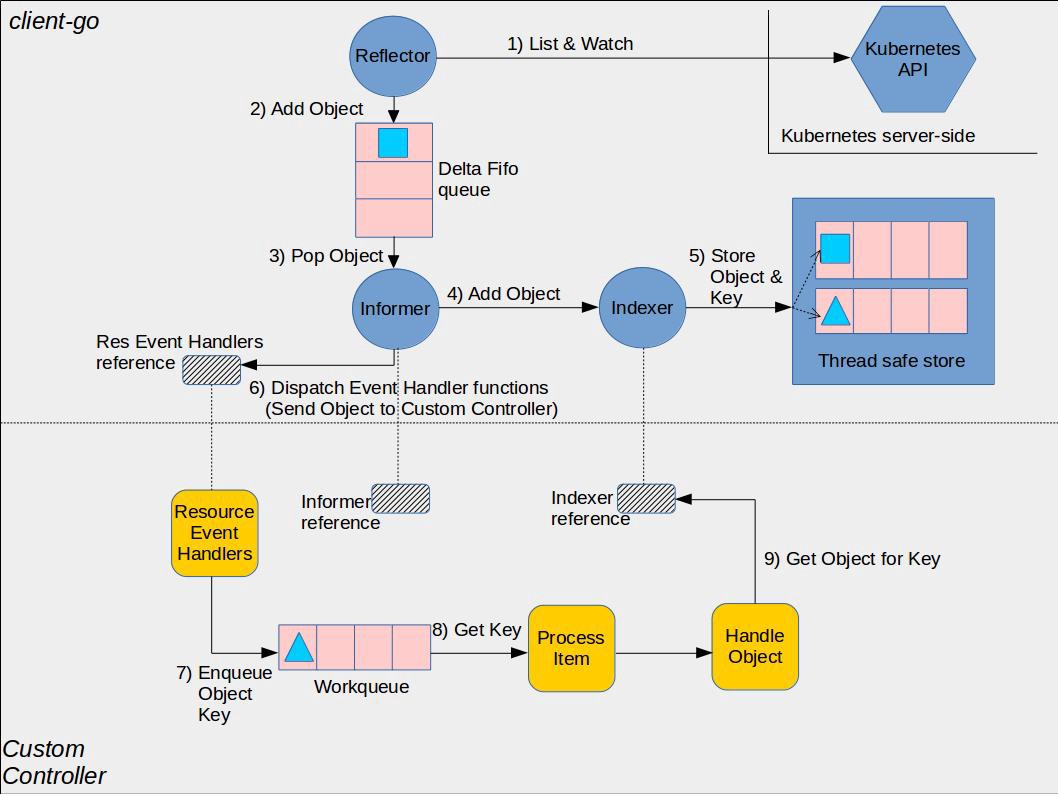
Informer 由三部分构成:
- Reflector:Informer 通过 Reflector 与 Kubernetes apiserver 建立连接并 ListAndWatch Kubernetes 资源对象的变化,并将此“增量” push 入 DeltaFIFO Queue
- DeltaFIFO Queue:Informer 从该队列中 pop 增量,或创建或更新或删除本地缓存(Local Store)
- Indexer:将增量中的 Kubernetes 资源对象保存到本地缓存中,并为其创建索引,这份缓存与 etcd 中的数据是完全一致的。控制器只从本地缓存通过索引读取数据,这样做减小了 apiserver 和 etcd 的压力。
Reflector
当 Informer 启动时 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/controller.go#L127-L#132 会实例化一个 Reflector。我们先找到 Reflector 的定义 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/reflector.go#L48-L98 和 Reflector 的启动方法 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/reflector.go#L171-L182:
func (r *Reflector) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
klog.V(2).Infof("Starting reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
wait.BackoffUntil(func() {
if err := r.ListAndWatch(stopCh); err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(err)
}
}, r.backoffManager, true, stopCh)
klog.V(2).Infof("Stopping reflector %s (%s) from %s", r.expectedTypeName, r.resyncPeriod, r.name)
}
最主要的就是 ListAndWatch 方法 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/reflector.go#L207-L441
// ListAndWatch first lists all items and get the resource version at the moment of call,
// and then use the resource version to watch.
// It returns error if ListAndWatch didn't even try to initialize watch.
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
if err := func() error {
initTrace := trace.New("Reflector ListAndWatch", trace.Field{"name", r.name})
defer initTrace.LogIfLong(10 * time.Second)
var list runtime.Object
var paginatedResult bool
var err error
listCh := make(chan struct{}, 1)
panicCh := make(chan interface{}, 1)
go func() {
defer func() {
if r := recover(); r != nil {
panicCh <- r
}
}()
// Attempt to gather list in chunks, if supported by listerWatcher, if not, the first
// list request will return the full response.
pager := pager.New(pager.SimplePageFunc(func(opts metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
return r.listerWatcher.List(opts)
}))
// a lot of code here
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), options)
if isExpiredError(err) || isTooLargeResourceVersionError(err) {
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(true)
// Retry immediately if the resource version used to list is unavailable.
// The pager already falls back to full list if paginated list calls fail due to an "Expired" error on
// continuation pages, but the pager might not be enabled, the full list might fail because the
// resource version it is listing at is expired or the cache may not yet be synced to the provided
// resource version. So we need to fallback to resourceVersion="" in all to recover and ensure
// the reflector makes forward progress.
list, paginatedResult, err = pager.List(context.Background(), metav1.ListOptions{ResourceVersion: r.relistResourceVersion()})
}
close(listCh)
}()
// a lot of code here
r.setIsLastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable(false) // list was successful
initTrace.Step("Objects listed")
listMetaInterface, err := meta.ListAccessor(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Unable to understand list result %#v: %v", r.name, list, err)
}
resourceVersion = listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion()
initTrace.Step("Resource version extracted")
items, err := meta.ExtractList(list)
if err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Unable to understand list result %#v (%v)", r.name, list, err)
}
initTrace.Step("Objects extracted")
if err := r.syncWith(items, resourceVersion); err != nil {
return fmt.Errorf("%s: Unable to sync list result: %v", r.name, err)
}
initTrace.Step("SyncWith done")
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(resourceVersion)
initTrace.Step("Resource version updated")
return nil
}(); err != nil {
return err
}
// watch part
}
我们要看一下 controller 结构中的 Config.ListerWatcher 是怎么来的:在实例化 SharedIndexInformer 时 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/shared_informer.go#L193 会传入 ListerWatcher 参数,而 Kubernetes API 定义相关代码中(通过代码生成器生成)都有固定的 NewFilteredXXXInformer 函数,其中调用了 NewSharedIndexInformer,ListWatch 对象就是在初始化的。
// NewFilteredPodInformer constructs a new informer for Pod type.
// Always prefer using an informer factory to get a shared informer instead of getting an independent
// one. This reduces memory footprint and number of connections to the server.
func NewFilteredPodInformer(client kubernetes.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
ListFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (runtime.Object, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).List(context.TODO(), options)
},
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options)
},
},
&corev1.Pod{},
resyncPeriod,
indexers,
)
}
- 首先
r.listerWatcher.List获取所有资源数据- 调用 Kubernetes API 资源
NewFilteredXXXInformer时初始化ListWatch时传入的ListFunc函数,通过 ClientSet 客户端与 apiserver 交互并获取 XXX 资源列表数据;
- 调用 Kubernetes API 资源
listMetaInterface.GetResourceVersion获取资源版本号- 每个资源对象都有
ResourceVersion,当 Kubernetes 资源对象变化时,其资源版本也会发生变化
- 每个资源对象都有
meta.ExtractList将资源数据转换为资源对象列表r.syncWith将资源对象和资源版本号存储到 DeltaFIFO 队列中或替换掉已存在的资源r.setLastSyncResourceVersion设置最新的资源版本号
ListAndWatch 本质上就是通过 apiserver 的 List API 获取所有最新版本的 Kubernetes 资源对象;通过 Watch API 来监听所有这些资源对象的变化。
下面就来看下所谓的 Watch https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/reflector.go#L207-L411
// ListAndWatch first lists all items and get the resource version at the moment of call,
// and then use the resource version to watch.
// It returns error if ListAndWatch didn't even try to initialize watch.
func (r *Reflector) ListAndWatch(stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
// list
for {
// give the stopCh a chance to stop the loop, even in case of continue statements further down on errors
select {
case <-stopCh:
return nil
default:
}
timeoutSeconds := int64(minWatchTimeout.Seconds() * (rand.Float64() + 1.0))
options = metav1.ListOptions{
ResourceVersion: resourceVersion,
// We want to avoid situations of hanging watchers. Stop any wachers that do not
// receive any events within the timeout window.
TimeoutSeconds: &timeoutSeconds,
// To reduce load on kube-apiserver on watch restarts, you may enable watch bookmarks.
// Reflector doesn't assume bookmarks are returned at all (if the server do not support
// watch bookmarks, it will ignore this field).
AllowWatchBookmarks: true,
}
// start the clock before sending the request, since some proxies won't flush headers until after the first watch event is sent
start := r.clock.Now()
w, err := r.listerWatcher.Watch(options)
if err != nil {
switch {
case isExpiredError(err):
// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionExpired - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already
// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.
// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
case err == io.EOF:
// watch closed normally
case err == io.ErrUnexpectedEOF:
klog.V(1).Infof("%s: Watch for %v closed with unexpected EOF: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: Failed to watch %v: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err))
}
// If this is "connection refused" error, it means that most likely apiserver is not responsive.
// It doesn't make sense to re-list all objects because most likely we will be able to restart
// watch where we ended.
// If that's the case wait and resend watch request.
if utilnet.IsConnectionRefused(err) {
time.Sleep(time.Second)
continue
}
return nil
}
if err := r.watchHandler(start, w, &resourceVersion, resyncerrc, stopCh); err != nil {
if err != errorStopRequested {
switch {
case isExpiredError(err):
// Don't set LastSyncResourceVersionUnavailable - LIST call with ResourceVersion=RV already
// has a semantic that it returns data at least as fresh as provided RV.
// So first try to LIST with setting RV to resource version of last observed object.
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: watch of %v closed with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
default:
klog.Warningf("%s: watch of %v ended with: %v", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, err)
}
}
return nil
}
}
}
r.listerWatcher.Watch 毫无疑问要回调 NewFilteredXXXInformer 中初始化 ListWatch 时传入的 WatchFunc 函数。
我们还是以 Pod 这种 Kubernetes API 资源为例 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/informers/core/v1/pod.go#L55-L78
func NewFilteredPodInformer(client kubernetes.Interface, namespace string, resyncPeriod time.Duration, indexers cache.Indexers, tweakListOptions internalinterfaces.TweakListOptionsFunc) cache.SharedIndexInformer {
return cache.NewSharedIndexInformer(
&cache.ListWatch{
// list func code gere
WatchFunc: func(options metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
if tweakListOptions != nil {
tweakListOptions(&options)
}
return client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch(context.TODO(), options)
},
},
&corev1.Pod{},
resyncPeriod,
indexers,
)
}
再来看下 client.CoreV1().Pods(namespace).Watch 的实现 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/kubernetes/typed/core/v1/pod.go#L100-L113:
// Watch returns a watch.Interface that watches the requested pods.
func (c *pods) Watch(ctx context.Context, opts metav1.ListOptions) (watch.Interface, error) {
var timeout time.Duration
if opts.TimeoutSeconds != nil {
timeout = time.Duration(*opts.TimeoutSeconds) * time.Second
}
opts.Watch = true
return c.client.Get().
Namespace(c.ns).
Resource("pods").
VersionedParams(&opts, scheme.ParameterCodec).
Timeout(timeout).
Watch(ctx)
}
https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/rest/request.go#L625-L690
// Watch attempts to begin watching the requested location.
// Returns a watch.Interface, or an error.
func (r *Request) Watch(ctx context.Context) (watch.Interface, error) {
url := r.URL().String()
req, err := http.NewRequest(r.verb, url, r.body)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
req = req.WithContext(ctx)
req.Header = r.headers
client := r.c.Client
if client == nil {
client = http.DefaultClient
}
r.backoff.Sleep(r.backoff.CalculateBackoff(r.URL()))
resp, err := client.Do(req)
// a lot of code here
if resp.StatusCode != http.StatusOK {
defer resp.Body.Close()
if result := r.transformResponse(resp, req); result.err != nil {
return nil, result.err
}
return nil, fmt.Errorf("for request %s, got status: %v", url, resp.StatusCode)
}
contentType := resp.Header.Get("Content-Type")
mediaType, params, err := mime.ParseMediaType(contentType)
if err != nil {
klog.V(4).Infof("Unexpected content type from the server: %q: %v", contentType, err)
}
objectDecoder, streamingSerializer, framer, err := r.c.content.Negotiator.StreamDecoder(mediaType, params)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
frameReader := framer.NewFrameReader(resp.Body)
watchEventDecoder := streaming.NewDecoder(frameReader, streamingSerializer)
return watch.NewStreamWatcher(
restclientwatch.NewDecoder(watchEventDecoder, objectDecoder),
// use 500 to indicate that the cause of the error is unknown - other error codes
// are more specific to HTTP interactions, and set a reason
errors.NewClientErrorReporter(http.StatusInternalServerError, r.verb, "ClientWatchDecoding"),
), nil
}
很典型的 Golang HTTP 请求代码,但是 Kubernetes apiserver 首次应答的 HTTP Header 中会携带上 Transfer-Encoding: chunked,表示分块传输,客户端会保持这条 TCP 连接并等待下一个数据块。如此 apiserver 会主动将监听的 Kubernetes 资源对象的变化不断地推送给客户端:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Transfer-Encoding: chunked
{"type":"ADDED", "object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1",...}}
{"type":"ADDED", "object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1",...}}
{"type":"MODIFIED", "object":{"kind":"Pod","apiVersion":"v1",...}}
当 Watch 接收到数据,也就是资源对象发生了变化,就要做出相应的处理 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/reflector.go#L422-L498:
// watchHandler watches w and keeps *resourceVersion up to date.
func (r *Reflector) watchHandler(start time.Time, w watch.Interface, resourceVersion *string, errc chan error, stopCh <-chan struct{}) error {
eventCount := 0
// Stopping the watcher should be idempotent and if we return from this function there's no way
// we're coming back in with the same watch interface.
defer w.Stop()
loop:
for {
select {
case <-stopCh:
return errorStopRequested
case err := <-errc:
return err
case event, ok := <-w.ResultChan():
if !ok {
break loop
}
if event.Type == watch.Error {
return apierrors.FromObject(event.Object)
}
if r.expectedType != nil {
if e, a := r.expectedType, reflect.TypeOf(event.Object); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected type %v, but watch event object had type %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
if r.expectedGVK != nil {
if e, a := *r.expectedGVK, event.Object.GetObjectKind().GroupVersionKind(); e != a {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: expected gvk %v, but watch event object had gvk %v", r.name, e, a))
continue
}
}
meta, err := meta.Accessor(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
continue
}
newResourceVersion := meta.GetResourceVersion()
switch event.Type {
case watch.Added:
err := r.store.Add(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to add watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Modified:
err := r.store.Update(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to update watch event object (%#v) to store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Deleted:
// TODO: Will any consumers need access to the "last known
// state", which is passed in event.Object? If so, may need
// to change this.
err := r.store.Delete(event.Object)
if err != nil {
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to delete watch event object (%#v) from store: %v", r.name, event.Object, err))
}
case watch.Bookmark:
// A `Bookmark` means watch has synced here, just update the resourceVersion
default:
utilruntime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("%s: unable to understand watch event %#v", r.name, event))
}
*resourceVersion = newResourceVersion
r.setLastSyncResourceVersion(newResourceVersion)
eventCount++
}
}
watchDuration := r.clock.Since(start)
if watchDuration < 1*time.Second && eventCount == 0 {
return fmt.Errorf("very short watch: %s: Unexpected watch close - watch lasted less than a second and no items received", r.name)
}
klog.V(4).Infof("%s: Watch close - %v total %v items received", r.name, r.expectedTypeName, eventCount)
return nil
}
watchHandler 方法会判断资源对象的变化类型(增删改)并更新 DeltaFIFO 队列。这里的 r.store 为什么会是 DeltaFIFO 队列呢?
https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/reflector.go#L66
type Reflector struct {
// The destination to sync up with the watch source
store Store
}
是因为 Reflector 定义中的 store 字段是一个 Store interface。而在 Informer 开始运行时,这个 store 被设置为了 DeltaFIFO 队列对象 https://github.com/kubernetes/client-go/blob/v0.18.6/tools/cache/shared_informer.go#L336-L378:
func (s *sharedIndexInformer) Run(stopCh <-chan struct{}) {
defer utilruntime.HandleCrash()
fifo := NewDeltaFIFOWithOptions(DeltaFIFOOptions{
KnownObjects: s.indexer,
EmitDeltaTypeReplaced: true,
})
cfg := &Config{
Queue: fifo,
ListerWatcher: s.listerWatcher,
ObjectType: s.objectType,
FullResyncPeriod: s.resyncCheckPeriod,
RetryOnError: false,
ShouldResync: s.processor.shouldResync,
Process: s.HandleDeltas,
}
func() {
s.startedLock.Lock()
defer s.startedLock.Unlock()
s.controller = New(cfg)
s.controller.(*controller).clock = s.clock
s.started = true
}()
}
所以 Reflector 的主要作用是 List & Watch 某些资源对象,并将此“增量”事件 push 入一个 DeltaFIFO 队列。